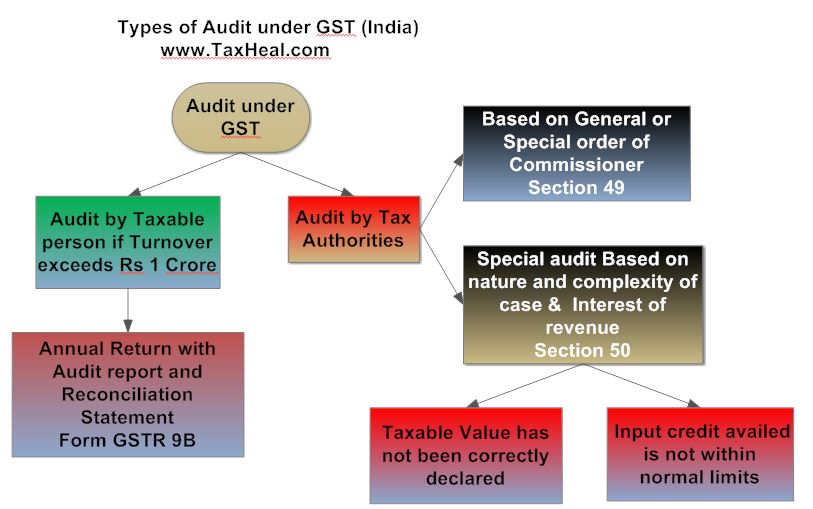
Audit under GST
Meaning of Audit under GST [ section 2(14)]
“Audit” means detailed examination of records, returns and other documents maintained or furnished by the taxable person under this Act or rules made thereunder or under any other law for the time being in force to verify, inter alia, the correctness of turnover declared, taxes paid, refund claimed and input tax credit availed, and to assess his compliance with the provisions of this Act or rules made thereunder;
Limit and Requirements of Audit by Taxable Person under GST
Every registered taxable person whose turnover during a financial year exceeds the prescribed limit [ note as per the draft rules Turnover limit is above Rs 1 core ] shall get his accounts audited by a chartered accountant or a cost accountant and shall submit to the proper officer a copy of the audited statement of accounts, the reconciliation statement and such other documents in the form and manner as may be prescribed in this behalf.[ section 44(4)]
Annual return with Audited annual Account and Reconciliation statement
Every taxable person who is required to get his accounts audited shall furnish, electronically, the annual return along with the audited copy of the annual accounts and a reconciliation statement, reconciling the value of supplies declared in the return furnished for the year with the audited annual financial
statement, and such other particulars as may be prescribed.
Annual Return has to be funrnished in Form GSTR 9B along with Reconciliation statement by 31st December of the next Financial Year
Rectification of Return based on results of Audit under GST
if any taxable person after furnishing a return discovers any omission or incorrect particulars therein, other than as a result of scrutiny, audit, inspection or enforcement activity by the tax authorities, he shall rectify such omission or incorrect particulars in the return to be filed for the month or quarter, as the case may be, during which such omission or incorrect particulars are noticed, subject to payment of interest, where applicable and as specified in the Act:
However no such rectification of any omission or incorrect particulars shall be allowed after the due date for filing of return for the month of September or second quarter, as the case may be, following the end of the financial year, or the actual date of filing of relevant annual return, whichever is earlier.
Who are the Tax authorities authorized to conduct audit of taxpayers under GST?
As per section 49 of Model GST Law , any officer of CGST or SGST authorized by his Commissioner by a general or specific order may conduct audit of a taxpayer. The frequency and manner of audit will be prescribed in due course.
Whether any prior intimation is required before conducting the audit under GST by Tax authorities ?
Yes, prior intimation is required and the taxable person should be informed at least 15 days prior to conduct of audit
What is the period within which the audit is to be completed in case of audit ordered by Tax authorities ?
The audit is required to be completed within 3 months from the date of commencement of audit or within a further period of a maximum of 6 months subject to the approval of the Commissioner.
What is meant by commencement of audit under GST ?
Ans. The term ‘commencement of audit’ is important because audit has to be completed within a given time frame in reference to this date of commencement. Commencement of audit means the later of the following:
| (a) | the date on which the records/accounts called for by the audit authorities are made available to them, or | |
| (b) | the actual institution of audit at the place of business of the taxpayer. |
What are the obligations of the taxable person when he receives the notice of audit under GST from Tax Authorities?
Ans. The taxable person is required to:
| (a) | facilitate the verification of accounts/records available or requisitioned by the authorities, | |
| (b) | provide such information as the authorities may require for the conduct of the audit, and | |
| (c) | render assistance for timely completion of the audit. |
What would be the action by the proper officer upon conclusion of the audit under GST ?
The proper officer must without delay inform the taxable person about his findings, reasons for findings and the taxable person’s rights and obligations in respect of such findings.
Under what circumstances can a special audit under GST be instituted?
A special audit can be instituted in limited circumstances where during scrutiny, investigation, etc. it comes to the notice that a case is complex or the revenue stake is high. This power is given in section 50 of Model GST Law. Special Audit can be ordered even if accounts of the taxable person have been audited under any other provision of this Act or any other law for the time being in force or otherwise.
The taxable person shall be given an opportunity of being heard in respect of any material gathered on the basis of special audit which is proposed to be used in any proceedings under this Act or rules made thereunder.
Who can serve the notice for special audit under GST?
The Assistant/Deputy Commissioner is to serve the notice for special audit only after prior approval of the Commissioner.
Who will do the special audit under GST ?
A Chartered Accountant or a Cost Accountant so nominated by the Commissioner may undertake the audit.
What is the time limit to submit the audit report under GST ?
The auditor will have to submit the report within 90 days or within the further extended period of 90 days.
Who will bear the cost of special audit under GST ?
The expenses for examination and audit including the remuneration payable to the auditor will be determined and borne by the Commissioner.
What action the tax authorities may take after the special audit under GST ?
Based on the findings/observations of the special audit, action can be initiated under section 51 of the Model GST Law .
Free Education Guide on Goods & Service Tax (GST)