New Syllabus for Foundation Programme
ICSI Notification No.4 (updated) of 2017 Introduction of New Syllabus for the Foundation Programme of the Company Secretaryship Course
The Council of the Institute of Company Secretaries of India in exercise of the powers vested under clause (a) of sub-section (2) of Section 15 of the Company Secretaries Act, 1980, as amended by the Company Secretaries (Amendment) Act, 2006 approved the Syllabus (2017) for the Foundation Programme of the Company Secretaryship Course, as under
• The Syllabus (2017) for Foundation Programme shall comprise of four papers.
PAPER 1: BUSINESS ENVIRONMENT AND LAW
PAPER 2: BUSINESS MANAGEMENT, ETHICS & ENTREPRENEURSHIP
PAPER 3: BUSINESS ECONOMICS
PAPER 4: FUNDAMENTALS OF ACCOUNTING AND AUDITING
• The mode of examination will be Computer based MCQs.
• The New Syllabus (2017)for the Foundation Programme shall be applicable for the students who register in Foundation Programme on or after 1st April 2017. The first examination under New Syllabus (2017) for Foundation Programme shall be conducted in June 2018. . The detailed contents for each of the Four papers of the Foundation Programme under the Syllabus (2017) and the switchover scheme as approved by the Council are as under:
Scheme of Papers
DETAILED SYLLABUS FOR FOUNDATION PROGRAMME
PAPER 1: BUSINESS ENVIRONMENT AND LAW
Level of Knowledge: Basic Knowledge
Objective: To give orientation about different forms of organizations, functions in organizations, business strategies and environment, along with an exposure to elements of business laws
PART A: BUSINESS ENVIRONMENT (40 MARKS)
1. Business Environment
Introduction and Features; Concepts of Vision & Mission Statements; Types of Environment-Internal to the Enterprise(Value System, Management Structure and Nature, Human Resource, Company Image and Brand Value, Physical Assets, Facilities, Research & Development, Intangibles, Competitive Advantage),External to the Enterprise(Micro- Suppliers, Customers, Market Intermediaries; Macro- Demography, Natural, Legal & Political, Technological, Economy, Competition, Socio-cultural and International); Business Environment with reference to Global Integration; Comparative Analysis of Business Environment: India and Other Countries
2. Forms of Business Organization
Concept and Features in relation to following business models- Sole Proprietorship; Partnership; Company; Statutory Bodies and Corporations; HUF and Family Business; Cooperatives, Societies and Trusts; Limited Liability Partnership; OPCs; Other Forms of Organizations.
3. Scales of Business
Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises; Large Scale Enterprises and Public Enterprises; MNCs
4. Emerging Trends in Business
Concepts, Advantages and Limitations-Franchising, Aggregators, Business Process Outsourcing (BPO) & Knowledge Process Outsourcing (KPO); E-Commerce, Digital Economy
5. Business Functions
Strategic- Planning, Budgetary Control, R&D, Location of a Business, Factors affecting Location, Decision Making and Government Policy; Supply Chain-Objectives, Importance, Limitations, Steps, Various Production Processes; Finance- Nature, Scope, Significance of Financial Management, Financial Planning (Management Decisions – Sources of Funds, Investment of Funds, Distribution of Profits); Marketing- Concept, Difference between Marketing and Selling, Marketing Mix, Functions of Marketing; Human Resources- Nature, Objectives, Significance; ServicesLegal, Secretarial, Accounting, Administration, Information and Communication Technology; Social Functions.
PART B: BUSINESS LAWS (60 MARKS)
6. Introduction to Law
Meaning of Law and its Significance; Relevance of Law to Modern Civilized Society; Sources of Law; Legal Terminology and Maxims; Understanding Citation of Cases
7. Elements of Company Law
Meaning and Nature of Company; Promotion and Incorporation of a Company; Familiarization with the Concept of Board of Directors, Shareholders and Company Meetings; Company Secretary; E-Governance
8. Elements of Law relating to Partnership and LLP
Nature of Partnership and Similar Organizations- Co-Ownership, HUF; Partnership Deed; Rights and Liabilities of Partners- New Admitted, Retiring and Deceased Partners; Implied Authority of Partners and its Scope; Registration of Firms; Dissolution of Firms and of the Partnership; Limited Liability Partnership Act.
9. Elements of Law relating to Contract
Meaning of Contract; Essentials of a Valid Contract; Nature and Performance of Contract; Termination and Discharge of Contract; Indemnity and Guarantee; Bailment and Pledge; Law of Agency
10. Elements of Law relating to Sale of Goods
Essentials of a Contract of Sale; Sale Distinguished from Agreement to Sell, Bailment, Contract for Work and Labour and Hire-Purchase; Conditions and Warranties; Transfer of Title by Non-Owners; Doctrine of Caveat Emptor; Performance of the Contract of Sale; Rights of Unpaid Seller.
11. Elements of Law relating to Negotiable Instruments
Definition of a Negotiable Instrument; Instruments Negotiable by Law and by Custom; Types of Negotiable Instruments; Parties to a Negotiable Instrument- Duties, Rights, Liabilities and Discharge; Material Alteration; Crossing of Cheques; Payment and Collection of Cheques and Demand Drafts; Presumption of Law as to Negotiable Instruments.
12. Elements of Information Technology Act
Cyberspace; Cyber laws; Scope of Cyber Laws; Classification of Cyber Crime; Information Technology Act 2000; Regulation of Certifying Authorities; Adjudication.
13. Role of CS- Duties and Responsibilities, Areas of Practice
Introduction; Role of Company Secretary under Companies Act, 2013- Role of Company Secretary in Employment, Role of Company Secretary in Practice; Recognition to Company Secretary in Practice under Various Laws.
PAPER 2: BUSINESS MANAGEMENT, ETHICS & ENTREPRENEURSHIP
Level of Knowledge: Basic Knowledge
Objective: To acquaint with the basic principles of management, ethics, communication techniques and entrepreneurship
PART A: BUSINESS MANAGEMENT (40 Marks)
Nature of Management and its Process
Meaning, Objectives, Importance; Nature of Management- Science, Art, Profession; Evolution of Management;
Management Functions- Planning, Organising, Personnel Management, Directing and Control; Principles of Management- Fayol and Taylor Principles; Managerial Skills; Task and Responsibilities of Professional Manager
1. Planning
Concept, Features, Importance, Limitations; Planning process; Types of Plans- Objectives, Strategy, Policy, Procedures, Method, Rule, Budget; Plan vsProgramme- Policies and Procedures; Decision making
2. Organizing
Concept, Features, Importance, Limitations; Organising process; Types of Organisation; Structure of Organisation; Centralisation and De-Centralisation; Delegation; Growth in Organisation
3. Human Resource Management
Concept, Features, Importance, Limitations; Recruitment process- Selection; Training and Development- Methods; Functions of Personnel Manager; Performance Management; Appraisal Methods; Human Resource Planning,; Talent Management; Organization Development
4. Direction and Co-ordination
Direction: Concept, Features, Importance, Limitations; Elements of Directing- Supervision, Motivation, Leadership, Communication; Co-Ordination-Concept, Features, Importance, Limitations; Co-Ordination Types- Internal and External; Co-Ordination- the Essence of Management
5. Controlling
Concept, Features, Importance, Limitations; Control process; Essentials of a Good Control System; Techniques of Control- Traditional and Non-Traditional Control devices; Relationship between Planning and Controlling
6. Recent Trends in Management
Change Management; Crisis Management; Total Quality Management; Risk Management; Global Practices
PART B: BUSINESS ETHICS (10 MARKS)
7. Business Ethics
Overview of Ethics in Business; Elements; Ethical principles in Business- Indian and Ancient Indian Perspective
PART C: BUSINESS COMMUNICATION (25 MARKS)
8. Business Communication
Concept, features, importance, limitations; means of Communication- Written, Oral, Visual, Audio Visual; Principles and Essentials of Business Communication; Process of Communication; Barriers to Communication
9. Essentials of Good English
Grammar and Usage; enriching vocabulary, words- multiple meaning, single word for a group of words, choice of words, words frequently misspelt, punctuations, prefix and suffix, parts of speech, articles; synonyms and antonyms, tenses, idioms and phrases; foreign words and phrases commonly used; abbreviations and numerals; pronunciation, Latin, French and Roman words used in abbreviated form; Legal Terminologies- idioms and phrases
10. Business Correspondence
Introduction; Meaning of Business Correspondence; Importance of Business Correspondence; Essential Qualities of a Good Business Letter; Parts of a Business Letter; Types of Business Letters; Human Resource; Purchase; Sales; Accounts
11. Interdepartmental Communication
Internal memos; messages through Electronic Media; Public Notices and Invitations; Representations to Trade Associations, Chambers of Commerce and Public Authorities
12. E Correspondence
Concept of E-Correspondence: Web, Internet; Concept of e-mail- History of E-mail, Features; Electronic Mail Systemoptimizing personal e-mail use, proper E-mail Correspondence, E-Mail Etiquette; Advantages and Disadvantages of E-mail; Intranet- Benefits of Intranet, Purpose of Intranet
PART D: ENTREPRENEURSHIP (25 MARKS)
13. Entrepreneurship
Four Key elements of Entrepreneurship; Traits of an Entrepreneur; Characteristics of an Entrepreneur; Who is an Entrepreneur; Why Entrepreneurship; Types of Entrepreneur
14. Entrepreneurship-Creativity and Innovation
Creativity and Innovation in an Entrepreneurial organisation; Tools for Environment Scanning- SWOT Analysis, PESTLE Analysis, Porters approach to Industry Analysis; Environmental Scanning Process; Types of Environmental Scanning; Market Assessment; Assessment of Business Opportunities- Developing Effective Business Plans, identification and evaluation of the opportunity, Determination of the required Resources, management of the resulting enterprise
15. Growth and Challenges of Entrepreneurial Ventures
Entrepreneurial opportunities in contemporary business environment; Strategic Planning for emerging ventureFinancing the entrepreneurial Business, Resource Assessment- Financial and Non-Financial; Fixed and Working Capital Requirement; Funds flow; Sources and means of Finance; Managing the growing Business- Effecting Change, Modernization, Expansion and Diversification
16. Social Entrepreneurship
Introduction; Definition of Social Entrepreneurship; Who is a Social Entrepreneur; how to identify a Social Entrepreneurship Opportunity; Creating a social business model; Funding social ventures; Strategies for success; Challenges for the Indian Social Enterprise Sector
17. Government Initiatives for Business Development
Skill India; Ease of Business; Start Up India; Stand Up India
PAPER 3: BUSINESS ECONOMICS
Level of Knowledge: Basic Knowledge
Objective: To familiarize the basic concepts and theories of economics, elementary statistics and mathematics.
PART A: ECONOMICS (80 MARKS)
1. The Fundamentals of Economics
The Economic Problem-Scarcity and Choice; Nature and Scope- Positive and Normative Economics, Micro and Macro Economics; Central Problems of an Economy; Production Possibility Curve; Opportunity Cost; Working of Economic Systems; Economic Cycles
2. Basic Elements of Demand and Supply
Demand- Meaning, Demand Schedule, Individual and Market Demand Curve, Determinants of Demand, Law of Demand, Changes in Demand; Supply- Meaning, Supply Schedule, Individual and Market Supply Curve, Determinants of Supply, Law of Supply, Changes in Supply; Equilibrium of Demand and Supply- Determination of Equilibrium Price and Quantity, Effect of a shift in Demand or Supply; Elasticity of Demand and Supply
3. Theory of Consumer Behaviour
Cardinal Utility Approach-Law of Diminishing Marginal Utility, Law of Equi-Marginal Utility; Indifference Curve Approach- Indifference Curves, Properties of Indifference Curves, Budget Line, Consumer’s Equilibrium
4. Theory of Production and Costs
Theory of Production- Factors of Production, Basic Concepts, Production Function, Law of Variable Proportions, Returns to Scale; Producer’s Equilibrium- Least-Cost Factor Combination and Output Maximisation for a given Level of Outlay; Theory of Costs- Basic Concepts, Short-run Total Cost Curves- Fixed and Variable, Short-run Average and Marginal Cost Curves, Relationship between Average and Marginal Cost Curve, Average and Marginal Cost Curves in the Long-run
5. Analysis of Markets
Basic Concepts of Revenue, Revenue Curves, Relationship between Average and Marginal Revenue Curve; Concept of Market and Main Forms of Market; Equilibrium of the Firm- Meaning, Objectives of the Firm, Total Revenue-Total Cost Approach, Marginal Revenue-Marginal Cost Approach; Price and Output under Determination Perfect Competition, Monopoly, Monopolistic Competition and Oligopoly.
6. Indian Economy- An Overview
Basic Characteristics of the Indian Economy; Major Issues of Development; Development Experience and Recent Trends in Indian Economy; Indian Economy in Comparison to Major Economies of the World.
7. Basic Elements of Money and Banking
Concept of Money-Its Functions, Quantity Theory of Money, Credit Creation; Central Bank (Reserve Bank of India)- Role and Functions; Commercial Banks-Role and Functions; Basic Elements of E-Banking; Monetary Policy in India.
PART B: ELEMENTARY STATISTICS (20 MARKS)
8. Descriptive Statistics
Statistics- Definition, Functions, Scope, Application in Business, Law of Statistics, Limitations of Statistics; Collection and Presentation of Statistical Data-Primary and Secondary Data, Classification and Tabulation, Frequency Distribution, Cross Tabulation; Diagrams and Graphs; Measures of Central Tendency-Mean, Median, Mode; Measures of Dispersion-Mean Deviation, Standard Deviation, Range, Coefficient of Variation; Bi-variate AnalysisCovariance, Coefficient of Correlation.
9. Mathematics of Finance and Elementary Probability
Mathematics of Finance-Simple Interest, Compound Interest; Time Value of Money-Compounding & Discounting, Present Value & Future Value of an Annuity; Probability- Random Experiments, Sample Spaces, Events and Probability, Approaches to Probability- Classical & Empirical; Expected Value.
PAPER 4: FUNDAMENTALS OF ACCOUNTING AND AUDITING
Level of Knowledge: Basic Knowledge
Objective: To familiarize and develop an understanding of the basic aspects of accounting, auditing concepts and their principles
PART A: FUNDAMENTALS OF ACCOUNTING (70 MARKS)
1. Theoretical Framework
Meaning and Scope of Accounting; Accounting Concepts; Accounting Principles, Conventions and Standards – Concepts, Objectives, Benefits; Accounting Policies; Accounting as a Measurement Discipline – Valuation Principles, Accounting Estimates
2. Accounting Process
Documents & Books of Accounts- Invoice, Vouchers, Debit & Credit Notes, Day books, Journals, Ledgers and Trial Balance; Capital and Revenue- Expenditures and Receipts; Contingent Assets and Contingent Liabilities; Rectification of Errors
3. Bank Reconciliation Statement
Meaning; Causes of difference between Bank Book Balance and Balance as per Bank Pass Book /Bank Statement; Need of Bank Reconciliation Statement; Procedure for Preparation of Bank Reconciliation Statement
4. Depreciation Accounting
Brief of various Methods; Computation and Accounting Treatment of Depreciation (Straight line and Diminishing Balance Method); Change in Depreciation Methods
5. Preparation of Final Accounts for Sole Proprietors
Preparation of Profit & Loss Account; Balance Sheet
6. Partnership Accounts
Goodwill- Nature of Goodwill and Factors Affecting Goodwill; Methods of Valuation- Average Profit, Super Profit and Capitalization Methods; Treatment of Goodwill; Final Accounts of Partnership Firms- Admission of a Partner, Retirement/Death of a Partner, Dissolution of a Partnership Firm; Joint Venture and Consignment Account
7. Introduction to Company Accounts
Issue of Shares and Debentures; Forfeiture of Shares; Re-Issue of Forfeited Shares; Redemption of Preference Shares
8. Accounting for Non-Profit Organizations
Receipt and Payment Accounts; Income and Expenditure Accounts
9. Computerized accounting environment
Basic Utility of SAP, TALLY, ERP
PART B: FUNDAMENTALS OF AUDITING (30 MARKS)
10. Auditing
Concepts and Objectives; Principles of Auditing; Types of Audit; Evidence in Auditing; Audit Programmes
11. Audits and Auditor’s Reports
Internal Audit; Statutory Auditor- Appointment, Qualification, Rights and Duties; Secretarial Audit- An Overview; Cost Audit- An Overview; Reporting- Types, Meaning, Contents, Qualifications
******
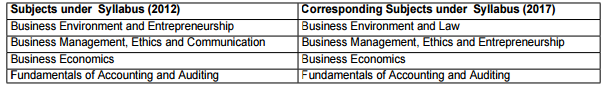
Scheme of Paperwise Exemptions for Switch over from Syllabus (2012) to Syllabus (2017) for Foundation Programme Examination
• All candidates registered under Syllabus (2012), enrolled for the Foundation Programme examination shall be examined under Syllabus (2017), from June 2018 session onwards, i.e., candidates shall be compulsorily switched over from Syllabus (2012) to Syllabus (2017) for Foundation Programme Examination with effect from June 2018.
Paperwise Exemption Scheme
• The Scheme of Paper-wise Exemption in corresponding subjects for switching over from Syllabus (2012) to Syllabus (2017) for Foundation Programme shall be as under:
• The students under Syllabus (2012) compulsorily switched over to Syllabus (2017) would be provided with Study Material free of cost for Foundation Programme under Syllabus (2017) in their respective subjects.
Qualifying Marks
• The qualifying marks for Foundation Programme Examination will remain as per Regulation 39A(3) of The Company Secretaries Regulations, 1982, as under:
A candidate shall be declared to have passed in the Foundation Programme Examination if he obtains at one sitting a minimum of forty per cent marks in each subject and fifty per cent marks in the aggregate of all subjects.
Provided that a candidate who has appeared in all the subjects for which he was enrolled and has obtained sixty per cent marks or above in any subject, but failed shall be declared to have passed in the subsequent examination if he obtains a minimum of forty per cent marks in each remaining subject and fifty per cent marks in the aggregate of the remaining subjects at one sitting within the next three following examinations.
Qualification Based Exemption Scheme
All graduates or post graduates (excluding fine arts) and those passed in the Foundation Examination of The Institute of Cost Accountants of India (ICAI-CMA) or CPT Examination of The Institute of Chartered Accountants of India (ICAI) or of any other accountancy institution in India or abroad recognized as equivalent thereto by the Council of the Institute shall be exempted from passing the Foundation Programme Examination. Such students may directly seek registration to Executive Programme of Company Secretaryship Course.
By order of the Council
CS Dinesh C. Arora
Secretary